Tiger Cloud: Performance, Scale, Enterprise, Free
Self-hosted products
MST
Tiger Agents for Work is a Slack-native AI agent that you use to unify the knowledge in your company. This includes your Slack history, docs, GitHub repositories, Salesforce and so on. You use your Tiger Agent to get instant answers for real business, technical, and operations questions in your Slack channels.
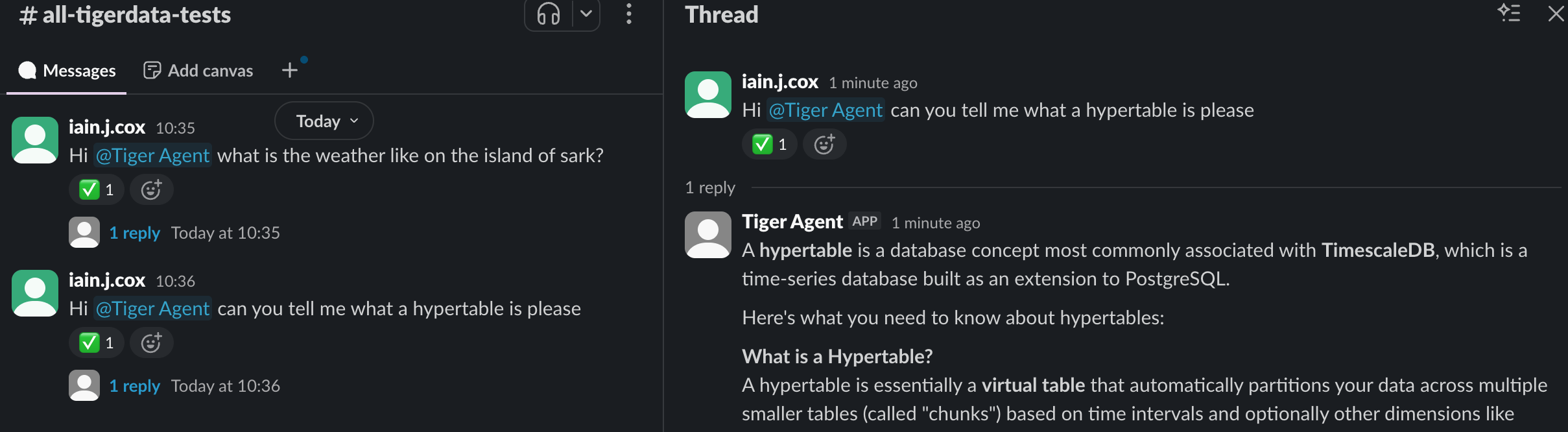
Tiger Agents for Work can handle concurrent conversations with enterprise-grade reliability. They have the following features:
- Durable and atomic event handling: Postgres-backed event claiming ensures exactly-once processing, even under high concurrency and failure conditions
- Bounded concurrency: fixed worker pools prevent resource exhaustion while maintaining predictable performance under load
- Immediate event processing: Tiger Agents for Work provide real-time responsiveness. Events are processed within milliseconds of arrival rather than waiting for polling cycles
- Resilient retry logic: automatic retry with visibility thresholds, plus stuck or expired event cleanup
- Horizontal scalability: run multiple Tiger Agent instances simultaneously with coordinated work distribution across all instances
- AI-Powered Responses: use the AI model of your choice, you can also integrate with MCP servers
- Extensible architecture: zero code integration for basic agents. For more specialized use cases, easily customize your agent using Jinja templates
- Complete observability: detailed tracing of event flow, worker activity, and database operations with full Logfire
instrumentation
This page shows you how to install the Tiger Agent CLI, connect to the Tiger Data MCP server, and customize prompts for your specific needs.
To follow the procedure on this page you need to:
Create a Tiger Cloud account.
This procedure also works for self-hosted TimescaleDB.
- Install the uv package manager
- Get an Anthropic API key
- Optional: get a Logfire token
Before installing Tiger Agents for Work, you need to create a Slack app that the Tiger Agent will connect to. This app provides the security tokens for Slack integration with your Tiger Agent:
Create a manifest for your Slack App
In a temporary directory, download the Tiger Agent Slack manifest template:
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/timescale/tiger-agents-for-work/main/slack-manifest.jsonEdit
slack-manifest.jsonand customize your name and description of your Slack App. For example:"display_information": {"name": "Tiger Agent","description": "Tiger AI Agent helps you easily access your business information, and tune your Tiger services","background_color": "#000000"},"features": {"bot_user": {"display_name": "Tiger Agent","always_online": true}},Copy the contents of
slack-manifest.jsonto the clipboard:cat slack-manifest.json| pbcopy
Create the Slack app
- Go to api.slack.com/apps
.
- Click
Create New App. - Select
From a manifest. - Choose your workspace, then click
Next. - Paste the contents of
slack-manifest.jsonand clickNext. - Click
Create.
- Go to api.slack.com/apps
Generate an app-level token
- In your app settings, go to
Basic Information. - Scroll to
App-Level Tokens. - Click
Generate Token and Scopes. - Add a
Token Name, then clickAdd Scope, addconnections:writethen clickGenerate. - Copy the
xapp-*token locally and clickDone.
- In your app settings, go to
Install your app to a Slack workspace
- In the sidebar, under
Settings, clickInstall App. - Click
Install to <workspace name>, then clickAllow. - Copy the
xoxb-Bot User OAuth Token locally.
- In the sidebar, under
You have created a Slack app and obtained the necessary tokens for Tiger Agent integration.
Tiger Agents for Work are a production-ready library and CLI written in Python that you use to create Slack-native AI agents. This section shows you how to configure a Tiger Agent to connect to your Slack app, and give it access to your data and analytics stored in Tiger Cloud.
Create a project directory
mkdir my-tiger-agentcd my-tiger-agentCreate a Tiger Agent environment with your Slack, AI Assistant, and database configuration
Download
.env.sampleto a local.envfile:curl -L -o .env https://raw.githubusercontent.com/timescale/tiger-agent/refs/heads/main/.env.sampleIn
.env, add your Slack tokens and Anthropic API key:# Slack tokens (from the Slack app you created)SLACK_APP_TOKEN=xapp-your-app-tokenSLACK_BOT_TOKEN=xoxb-your-bot-token# Anthropic API keyANTHROPIC_API_KEY=sk-ant-your-api-key# Optional: Logfire token for enhanced loggingLOGFIRE_TOKEN=your-logfire-tokenAdd the connection details for the Tiger Cloud service you are using for this Tiger Agent:
PGHOST=<host>PGDATABASE=tsdbPGPORT=<port>PGUSER=tsdbadminPGPASSWORD=<password>Save and close
.env.
Add the default Tiger Agent prompts to your project
mkdir promptscurl -L -o prompts/system_prompt.md https://raw.githubusercontent.com/timescale/tiger-agent/refs/heads/main/prompts/system_prompt.mdcurl -L -o prompts/user_prompt.md https://raw.githubusercontent.com/timescale/tiger-agent/refs/heads/main/prompts/user_prompt.mdInstall Tiger Agents for Work to manage and run your AI-powered Slack bots
Install the Tiger Agent CLI using uv.
uv tool install --from git+https://github.com/timescale/tiger-agents-for-work.git tiger-agenttiger-agentis installed in~/.local/bin/tiger-agent. If necessary, add this folder to yourPATH.Verify the installation.
tiger-agent --helpYou see the Tiger Agent CLI help output with the available commands and options.
Connect your Tiger Agent with Slack
Run your Tiger Agent:
tiger-agent run --prompts prompts/ --env .envIf you open the explorer in Tiger Cloud Console
, you can see the tables used by your Tiger Agent.
In Slack, open a public channel app and ask Tiger Agent a couple of questions. You see the response in your public channel and log messages in the terminal.
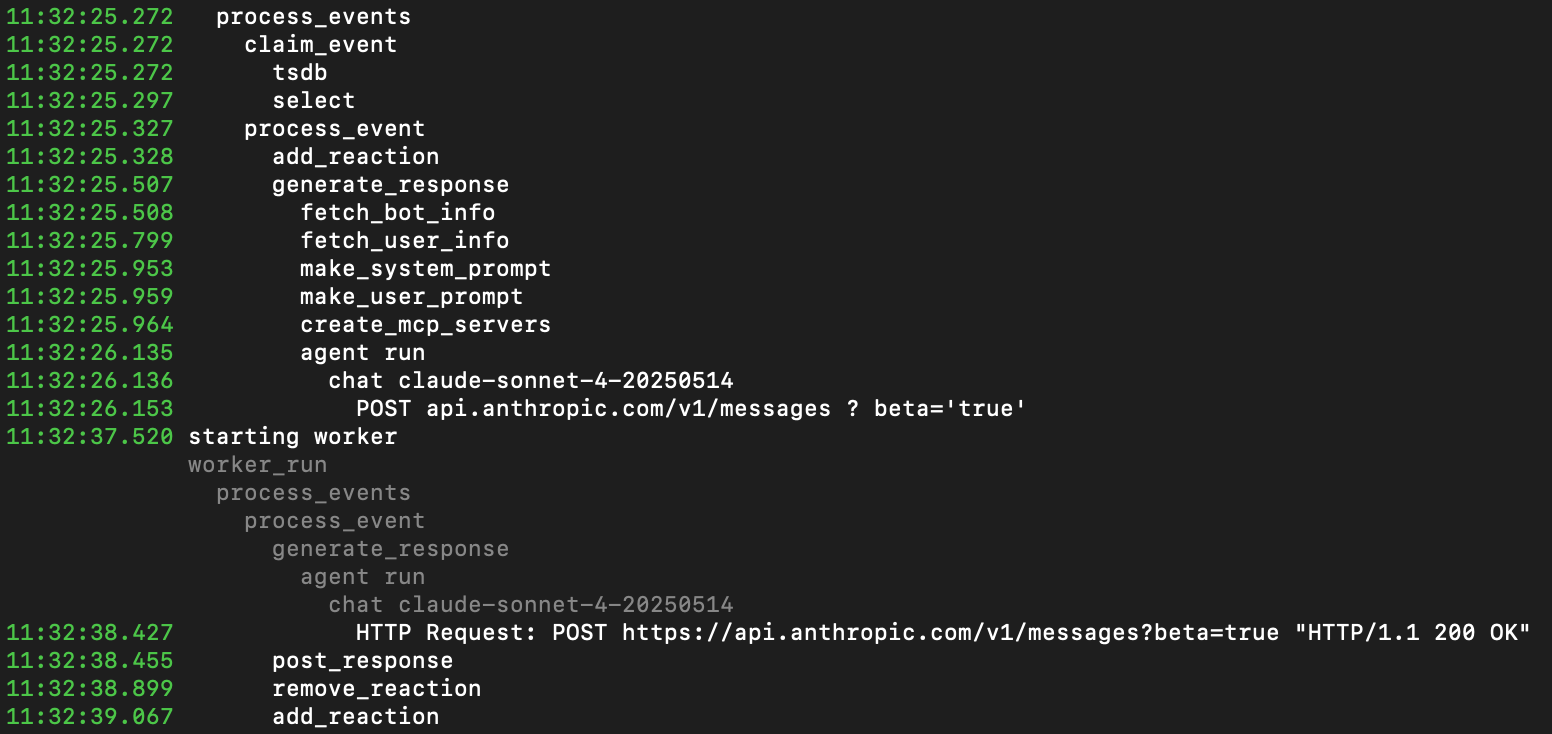
To increase the amount of specialized information your AI Assistant can use, you can add MCP servers supplying data your users need. For example, to add the Tiger Data MCP server to your Tiger Agent:
Copy the example
mcp_config.jsonto your projectIn
my-tiger-agent, run the following command:```bashcurl -L -o mcp_config.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/timescale/tiger-agent/refs/heads/main/examples/mcp_config.json```Configure your Tiger Agent to connect to the most useful MCP servers for your organization
For example, to add the Tiger Data documentation MCP server to your Tiger Agent, update the docs entry to the following:
"docs": {"tool_prefix": "docs","url": "https://mcp.tigerdata.com/docs","allow_sampling": false},To avoid errors, delete all entries in
mcp_config.jsonwith invalid URLs. For example thegithubentry withhttp://github-mcp-server/mcp.Restart your Tiger Agent
tiger-agent run --prompts prompts/ --mcp-config mcp_config.json
You have configured your Tiger Agent to connect to the Tiger MCP Server. For more information,
see MCP Server Configuration.
Tiger Agents for Work uses Jinja2 templates for dynamic, context-aware prompt generation. This system allows for sophisticated prompts that adapt to conversation context, user preferences, and event metadata. Tiger Agents for Work uses the following templates:
system_prompt.md: defines the AI Assistant's role, capabilities, and behavior patterns. This template sets the foundation for the way your Tiger Agent will respond and interact.user_prompt.md: formats the user's request with relevant context, providing the AI Assistant with the information necessary to generate an appropriate response.
To change the way your Tiger Agents interact with users in your Slack app:
Update the prompt
For example, in
prompts/system_prompt.md, add another item in theResponse Protocolsection to fine tune the behavior of your Tiger Agents. For example:5. Be snarky but vaguely amusingTest your configuration
Run Tiger Agent with your custom prompt:
tiger-agent run --mcp-config mcp_config.json --prompts prompts/
For more information, see Prompt tempates.
For additional customization, you can modify the following Tiger Agent parameters:
--model: change AI model (default:anthropic:claude-sonnet-4-20250514)--num-workers: adjust concurrent workers (default:5)--max-attempts: set retry attempts per event (default:3)
Example with custom settings:
tiger-agent run \--model claude-3-5-sonnet-latest \--mcp-config mcp_config.json \--prompts prompts/ \--num-workers 10 \--max-attempts 5
Your Tiger Agents are now configured with Tiger Data MCP server access and personalized prompts.
Keywords
Found an issue on this page?Report an issue or Edit this page
in GitHub.